The "Kibana server is not ready yet" error can bring your data visualization workflows to a screeching halt. This frustrating message often appears when you're eager to dive into your Elasticsearch data, leaving you stuck at the login screen. But don't worry — we've got you covered with a comprehensive guide to diagnose, fix, and prevent this common Kibana hiccup.
Understanding the "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" Error
The "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" error is a common issue encountered by users when the Kibana service, part of the Elastic Stack (ELK Stack), is unable to fully initialize and start serving requests. This error message typically indicates that Kibana is in the process of starting up but has encountered delays or problems in reaching a ready state.
Typical Scenarios When Users Encounter This Error
- Elasticsearch Connectivity Issues: Kibana relies on Elasticsearch as its backend. If Kibana cannot connect to the Elasticsearch cluster due to network issues or misconfigurations, the server may remain in a not-ready state.
- Configuration Errors: Errors in the Kibana configuration file (e.g.,
kibana.yml) can prevent proper initialization. - Resource Constraints: Insufficient system resources, such as memory or CPU, can delay Kibana’s startup.
- Version Mismatch: A mismatch between Kibana and Elasticsearch versions can result in compatibility issues, causing the error.
- Index Corruption: Problems with Kibana’s index in Elasticsearch (e.g.,
.kibanaindex) can lead to startup issues.
Importance of Kibana in the ELK Stack Ecosystem
Kibana serves as the visualization and analysis layer of the ELK Stack. It allows users to explore and interact with data stored in Elasticsearch through dashboards, charts, and advanced search queries. Without a functional Kibana server, users lose access to these critical capabilities, disrupting workflows and decision-making processes.
Potential Impacts on Data Visualization and Analysis Workflows
- Loss of Real-Time Insights: A non-functional Kibana server prevents users from accessing real-time dashboards and visualizations, which are often critical for monitoring and operational decisions.
- Disrupted Analytics Pipelines: Teams relying on Kibana for regular reporting or data analysis may face delays, affecting productivity and timelines.
- Reduced Troubleshooting Efficiency: Kibana’s search and filtering capabilities are essential for diagnosing issues in Elasticsearch data. Without it, resolving problems can become more time-consuming.
By understanding the root causes and impacts of the "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" error, users can take proactive measures to resolve it and maintain seamless data visualization and analysis workflows.
Quick Fix: Steps to Resolve Kibana Server Issues
If you encounter the "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" error, follow these steps to diagnose and resolve the issue efficiently:
- Check Elasticsearch Connection and Status
Ensure that Elasticsearch is running and accessible from the server where Kibana is installed.
If Elasticsearch security features are enabled, accessing the cluster health API without authentication will result in a 401 Unauthorized error. Ensure you provide basic authentication credentials in the
curlcommand.Unauthenticated Request:
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty"Error Response:
{ "error" : { "root_cause" : [ { "type" : "security_exception", "reason" : "missing authentication credentials for REST request [/_cluster/health?pretty]", "header" : { "WWW-Authenticate" : [ "Basic realm=\"security\", charset=\"UTF-8\"", "ApiKey" ] } } ], "type" : "security_exception", "reason" : "missing authentication credentials for REST request [/_cluster/health?pretty]", "header" : { "WWW-Authenticate" : [ "Basic realm=\"security\", charset=\"UTF-8\"", "ApiKey" ] } }, "status" : 401 }Authenticated Request:
Include the username and password in the
curlcommand using the-uflag.curl -u username:password -X GET "http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty"Successful Response:
{ "cluster_name" : "docker-cluster", "status" : "green", "timed_out" : false, "number_of_nodes" : 1, "number_of_data_nodes" : 1, "active_primary_shards" : 35, "active_shards" : 35, "relocating_shards" : 0, "initializing_shards" : 0, "unassigned_shards" : 0, "delayed_unassigned_shards" : 0, "number_of_pending_tasks" : 0, "number_of_in_flight_fetch" : 0, "task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis" : 0, "active_shards_percent_as_number" : 100.0 }- Look for a "green" or "yellow" status. A "red" status indicates problems with the Elasticsearch cluster that need to be resolved.
- Verify Kibana and Elasticsearch Version Compatibility
- Kibana and Elasticsearch must have matching versions to work together.
- Check the versions installed on your system:
- Kibana: Run
kibana --versionor check the version in the Kibana UI. - Elasticsearch: Check the version via the Elasticsearch cluster health command or the logs.
- Kibana: Run
- Refer to the Elastic Compatibility Matrix to ensure compatibility.
- Review Kibana Configuration File (kibana.yml) Settings
- Open the
kibana.ymlfile, typically located in/etc/kibana/. - Ensure the following critical settings are correct:
Elasticsearch host URL: Verify that the
elasticsearch.hostsentry points to the correct Elasticsearch instance.elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]Server configuration: Check the
server.hostandserver.portsettings.Authentication: If security is enabled, confirm that the username and password for Kibana to connect to Elasticsearch are properly configured.
- Open the
- Restart Kibana Service and Allow Sufficient Time for Initialization
Restart the Kibana service using your system’s service manager:
sudo systemctl restart kibanaMonitor the Kibana logs to track its startup process:
sudo journalctl -u kibana -fAllow a few minutes for the service to initialize fully, especially on systems with limited resources or large Elasticsearch clusters.
Common Configuration Mismatches
Misconfigurations are a frequent cause of the "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" error. Here are some common issues to check and address:
- Incorrect Elasticsearch URL in Kibana Settings
Symptom: Kibana cannot establish a connection to Elasticsearch due to an incorrect URL in the
kibana.ymlconfiguration file.Solution: Verify and update the
elasticsearch.hostsentry inkibana.ymlto ensure it points to the correct Elasticsearch instance. Example:elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
- Firewall Blocking Communication Between Kibana and Elasticsearch
Symptom: Network issues prevent Kibana from reaching Elasticsearch.
Solution: Check your firewall settings to ensure the Elasticsearch port (default:
9200) is open and accessible from the Kibana server.sudo ufw allow 9200/tcp
- SSL/TLS Certificate Issues
Symptom: If SSL/TLS is enabled, improperly configured certificates can block secure communication between Kibana and Elasticsearch.
Solution: Ensure that the
elasticsearch.ssl.certificateandelasticsearch.ssl.keyentries inkibana.ymlare correctly configured and point to valid certificate files. Example:elasticsearch.ssl.certificate: /path/to/cert.pem elasticsearch.ssl.key: /path/to/key.pem
- Insufficient System Resources Allocated to Kibana
Symptom: Limited memory, CPU, or disk space causes Kibana to fail during startup.
Solution: Increase system resources allocated to Kibana. For example, adjust the heap size in the Kibana environment configuration:
export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=2048"Restart the Kibana service after making the change.
By addressing these common configuration mismatches, you can resolve many of the underlying causes of Kibana startup issues and ensure smooth operation.
Diagnosing Kibana Server Readiness Problems
When the "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" error occurs, diagnosing the root cause is essential. Here are the key steps to identify and resolve the issue:
1. Examining Kibana Log Files for Error Messages
Purpose: Kibana logs provide detailed information about its startup process and any encountered issues.
How to Check: Or, check the log file directly if configured (e.g.,
/var/log/kibana/kibana.log).sudo journalctl -u kibana -fWhat to Look For:
- Elasticsearch connectivity issues
- Configuration errors
- Resource limitations
2. Using curl Commands to Test Elasticsearch Connectivity
Purpose: Ensure Kibana can communicate with the Elasticsearch cluster.
Test Command:
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty"Expected Output: Look for a "green" or "yellow" cluster status. A "red" status indicates issues with the Elasticsearch cluster.
Check Version Compatibility: Confirm that the version matches the Kibana version.
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200"
3. Verifying Network Connectivity Between Kibana and Elasticsearch
- Purpose: Ensure there are no network issues preventing Kibana from accessing Elasticsearch.
- How to Check:
Use
pingto verify the Elasticsearch server is reachable:ping <elasticsearch-host>Use
telnetorcurlto confirm the Elasticsearch port (default:9200) is open:telnet <elasticsearch-host> 9200
- Firewall Check: Ensure firewalls or security groups allow traffic between Kibana and Elasticsearch.
4. Checking for Kibana Index Corruption or Deletion in Elasticsearch
Purpose: Kibana relies on the
.kibanaindex in Elasticsearch for its configuration and state. If this index is missing or corrupted, Kibana may fail to start.How to Check: Look for the
.kibanaindex in the output.curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v"Fixing Issues:
If the index is missing, recreate it by restarting Kibana (it should automatically regenerate the index).
For corruption, delete the index (data will be lost) and let Kibana recreate it: Restart Kibana afterward.
curl -X DELETE "http://localhost:9200/.kibana"
By following these diagnostic steps, you can identify the underlying cause of the "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" error and take the necessary corrective actions to restore functionality.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
When basic diagnostic steps fail to resolve the "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" error, advanced troubleshooting techniques may be necessary. These methods address more complex underlying issues:
- Analyzing Elasticsearch Cluster Health
Purpose: Ensure that the Elasticsearch cluster is in a healthy state, as Kibana relies on it for operations.
How to Check:
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty"What to Look For:
- "Red" status: Indicates critical issues in the cluster (e.g., shard allocation failures).
- Node count: Verify that all nodes in the cluster are operational.
Next Steps:
Resolve shard allocation issues by using the following command:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:9200/_cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true"Check Elasticsearch logs for detailed error messages.
- Investigating Potential Plugin Conflicts
- Purpose: Plugins installed in Kibana or Elasticsearch can sometimes introduce compatibility issues.
- How to Check:
Review the Kibana logs for plugin-related errors:
sudo journalctl -u kibana -fList installed plugins in Elasticsearch:
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/_cat/plugins?v"
- Next Steps:
Disable problematic plugins in the
kibana.ymlconfiguration file or uninstall them:sudo bin/kibana-plugin remove <plugin-name>Verify plugin compatibility with your versions of Kibana and Elasticsearch.
- Addressing Memory and CPU Utilization Issues
- Purpose: Insufficient resources can prevent Kibana from initializing properly.
- How to Check:
Monitor system resources:
topCheck for memory allocation issues in Kibana logs.
- Next Steps:
Increase available memory for Kibana:
export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=4096"Optimize Elasticsearch heap size (e.g., set to 50% of available memory):
export ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms2g -Xmx2g"Ensure the server has adequate CPU and memory resources for both Kibana and Elasticsearch.
Restart Kibana or Elasticsearch to ensure the changes take effect, and restart the respective services:
For Kibana:
sudo systemctl restart kibanaOr, if running manually:
./bin/kibanaFor Elasticsearch:
sudo systemctl restart elasticsearchOr, if running manually:
./bin/elasticsearch
- Resolving Index Template and Mapping Problems
- Purpose: Misconfigured or corrupt index templates can lead to issues with Kibana’s
.kibanaindex. - How to Check:
List index templates in Elasticsearch:
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/_template?pretty"Inspect the mappings of the
.kibanaindex:curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/.kibana/_mapping?pretty"
- Next Steps:
If an issue is identified, delete and recreate the
.kibanaindex:curl -X DELETE "http://localhost:9200/.kibana"Restart Kibana to allow it to regenerate the index with default templates.
- Purpose: Misconfigured or corrupt index templates can lead to issues with Kibana’s
Dealing with Docker-specific Challenges
Running Kibana in Docker environments introduces unique challenges. Addressing these effectively ensures smooth operations and prevents common errors. Below are some key areas to focus on:
- Container Networking Issues in Docker Environments
- Symptom: Kibana cannot connect to Elasticsearch when running in separate containers, but both containers are present on the same Docker network.
- Cause: Misconfigured Docker networking settings can prevent inter-container communication.
- Solution:
Ensure both containers are part of the same Docker network. This ensures they can resolve each other's container names as hostnames and establish proper connectivity.
docker network create elastic-network docker run --name elasticsearch --network elastic-network elasticsearch docker run --name kibana --network elastic-network kibanaUse container names as hostnames in the
kibana.ymlfile:elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://elasticsearch:9200"]
- Volume Mounting and Permission Problems
- Symptom: Kibana fails to start due to permission issues when mounting configuration or data volumes.
- Cause: The container’s user may not have the necessary permissions for the mounted host directories.
- Solution:
Ensure the directory permissions match the container’s requirements:
sudo chown 1000:1000 /path/to/host/directoryUse Docker’s
-userflag to run the container with specific user permissions:docker run --user $(id -u):$(id -g) -v /path/to/host/directory:/usr/share/kibana kibana
- Docker Compose Configuration Best Practices
- Symptom: Kibana and Elasticsearch services fail to communicate or start correctly in a Docker Compose setup.
- Solution:
Use the following example Docker Compose configuration to ensure proper setup:
services: elasticsearch: image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.10.2 container_name: elasticsearch environment: - discovery.type=single-node networks: - elastic-network kibana: image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.10.2 container_name: kibana depends_on: - elasticsearch environment: - ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://elasticsearch:9200 networks: - elastic-network networks: elastic-network: driver: bridgeRun
docker-compose upto start the services, ensuring proper connectivity and configuration.
- Troubleshooting Multi-Container Setups
- Symptom: Issues arise when running Kibana alongside other services like Logstash or custom applications.
- Solution:
Check inter-container communication using
docker execandcurl. If Elasticsearch security is enabled, add credentials:docker exec kibana curl -u username:password "http://elasticsearch:9200"Use Docker Compose health checks to ensure services are ready before dependent containers start:
healthcheck: test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://elasticsearch:9200"] interval: 30s timeout: 10s retries: 3
By addressing these Docker-specific challenges, you can optimize Kibana’s deployment in containerized environments, ensuring reliable performance and connectivity.
Preventing Future "Kibana Server Not Ready" Errors
To avoid recurring instances of the "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" error, consider implementing the following proactive measures:
1. Implementing Regular Health Checks and Monitoring
- Purpose: Regular health checks help identify potential issues early.
- How to Implement:
Use monitoring tools like SigNoz or Elastic APM to track system health.
Periodically query Elasticsearch cluster health:
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty"Monitor Kibana logs for errors or warnings.
2. Setting Up Alerts for Kibana and Elasticsearch Services
- Purpose: Alerts ensure that IT teams are notified promptly about any anomalies.
- How to Implement:
Configure alerting in Kibana using the built-in Watcher or third-party tools.
Example alert for Elasticsearch node issues:
{ "trigger": { "schedule": { "interval": "5m" } }, "input": { "search": { "request": { "indices": [".kibana"], "body": { "query": { "match_all": {} } } } } }, "actions": { "notify": { "logging": { "text": "Kibana service detected an anomaly." } } } }
3. Following Best Practices for Elastic Stack Upgrades
- Purpose: Ensures compatibility and smooth transitions during version updates.
- How to Implement:
- Always review the Elastic Stack Compatibility Matrix before upgrading.
- Perform upgrades in a staging environment to identify potential issues.
- Upgrade Elasticsearch before Kibana to maintain compatibility.
4. Optimizing Kibana and Elasticsearch Configurations for Performance
- Purpose: Proper configurations enhance stability and prevent resource-related issues.
- How to Implement:
Allocate sufficient heap size for Elasticsearch and Kibana:
export ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms2g -Xmx2g" export NODE_OPTIONS="--max-old-space-size=2048"Optimize Elasticsearch index settings for large datasets.
Regularly audit
kibana.ymlandelasticsearch.ymlconfigurations to ensure they meet current workload requirements.
By adopting these measures, you can reduce the risk of encountering "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" errors, ensuring smoother operations and better system reliability.
SigNoz as an Alternative
SigNoz is a modern, open-source observability platform that provides a compelling alternative to Kibana for monitoring and analyzing system performance. While Kibana excels in visualizing log data and integrating with Elasticsearch, SigNoz offers a more streamlined and focused approach to observability, particularly for metrics, traces, and logs in distributed systems.
Key Benefits of Using SigNoz as an Alternative to Kibana
Integrated Metrics and Logs: SigNoz combines metrics, traces, and logs into a single platform, unlike Kibana, which primarily focuses on log and visualization data from Elasticsearch. This integrated approach simplifies monitoring by offering a unified view of system health.
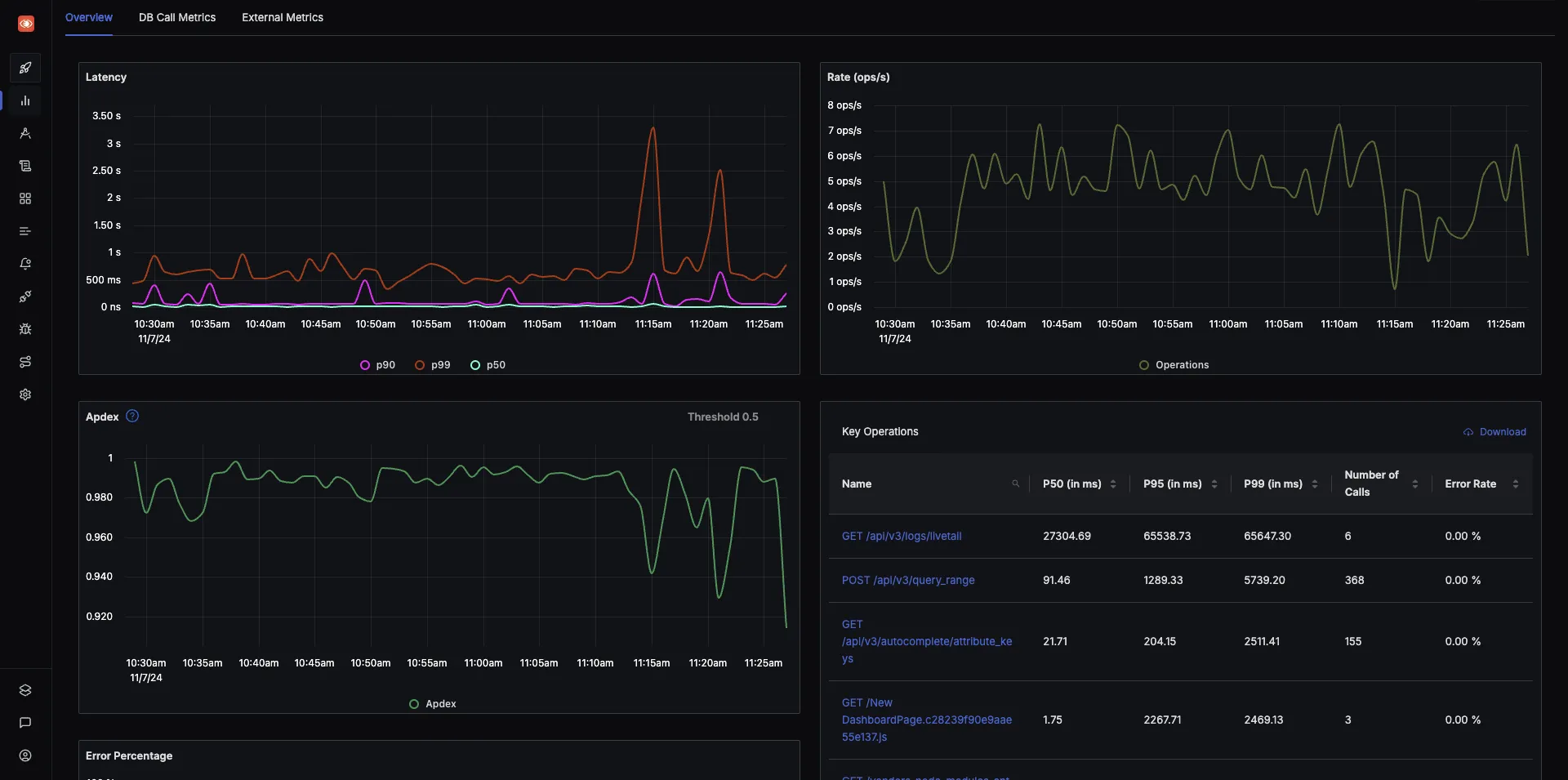
Measure things like application latency, requests per sec, error percentage and see your top endpoints with SigNoz. Real-Time Observability: SigNoz provides real-time insights into the performance and health of your systems, including infrastructure, services, and applications. This is especially useful for tracking resource usage, detecting slowdowns, and identifying performance issues in your system.
- User-Friendly Dashboards: SigNoz offers pre-built dashboards for monitoring a wide range of system metrics, making it easy to get started without needing to build complex visualizations. These dashboards cover metrics like CPU usage, memory consumption, network traffic, and application latency.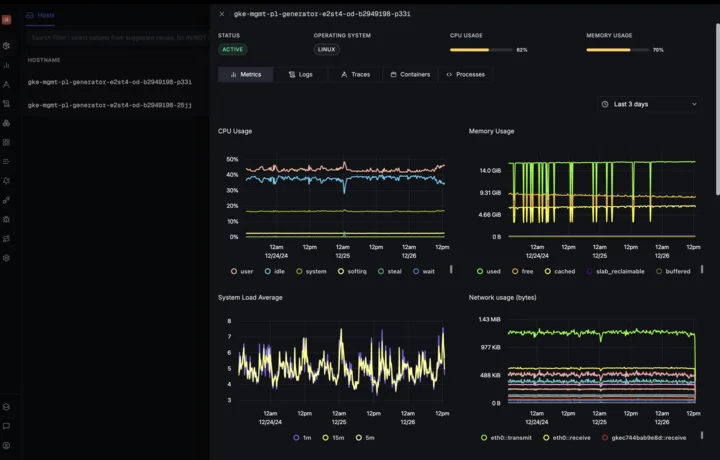
Distributed Tracing: SigNoz supports distributed tracing, allowing you to visualize and trace the flow of requests through various microservices, giving you a deeper understanding of how your system components are interacting.
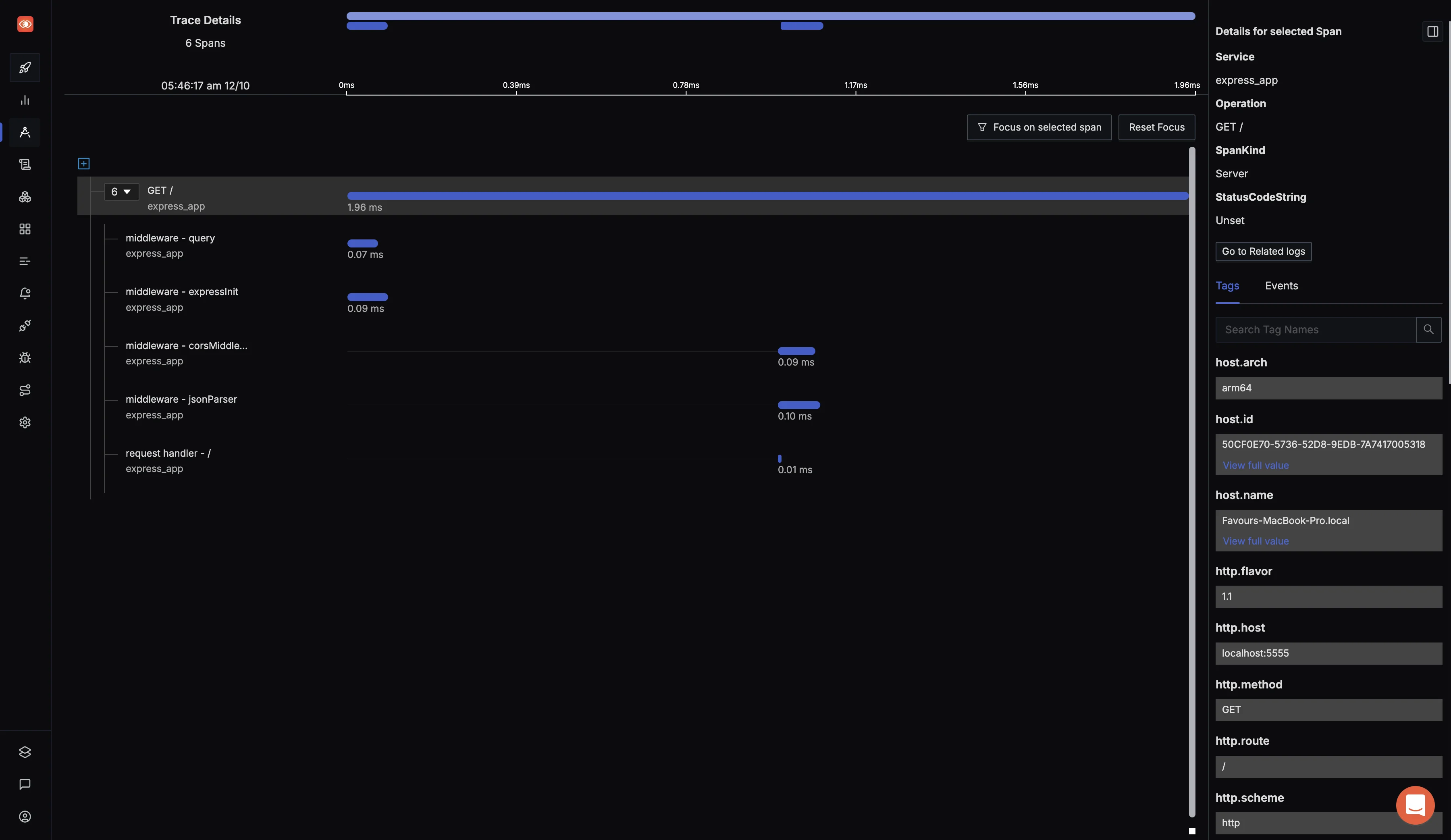
View of traces at a particular timestamp
To get started with monitoring your applications with SigNoz, check out our blog section.
SigNoz cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 19,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Key Takeaways
- The "Kibana server is not ready yet" error often stems from configuration or connectivity issues.
- Verify version compatibility and proper settings in
kibana.ymlto resolve most problems. - Examine log files and test Elasticsearch connectivity for accurate diagnosis.
- Regular monitoring and following best practices can prevent future occurrences.
- Tools like SigNoz help maintain Kibana server health proactively.
FAQs
How long should I wait for Kibana to become ready?
Typically, Kibana should be ready within a few minutes. If it takes longer than 5-10 minutes, investigate potential issues.
Can a firewall cause the "Kibana Server Is Not Ready Yet" error?
Yes, firewall settings can block communication between Kibana and Elasticsearch, causing this error.
What should I do if Kibana and Elasticsearch versions mismatch?
Update either Kibana or Elasticsearch to ensure version compatibility. Always use matching versions for optimal performance.
How can I check if the Kibana index is corrupt in Elasticsearch?
Use the Elasticsearch API to check the status of the .kibana index. If corrupt, you may need to reindex or restore from a backup.